Do you know what exactly does a UX (User Experience) Designer or UX specialist do? If you think it is all about creating simple & visually appealing interface, this article is specially designed for you, which we will discuss on how UX in many ways can bring values to users & businesses.
In this Article
If you are completely new to the world of ‘UX’, you may also take a look at our specially curated UX Guide for Business.
Over the past many years, we’re privileged to have worked with organization of all sizes in Asia, ranging from Fortune 500 MNCs, to government agencies and startups. Although we started to see more organizations adopting UX as part of business strategy, most of the enterprises still have the misconception of ‘UX is just about having good-looking and user friendly products’.
Credits: https://careerfoundry.com/en/blog/ux-design/the-difference-between-ux-and-ui-design-a-laymans-guide/
Such misconception also contributed to the rising number of ‘UI/UX designer’ hiring by companies, often with the roles of just doing graphic & visual design, neglecting other important UX roles, especially the user researcher. If you try to search for ‘UX Designer’ in the largest job portal of your country (in this case, we used Jobstreet for Southeast Asia market), it would be no surprise that most of the job description is about web graphic design, and the ‘preferred bonus skill’ is usually front-end coding skill: HTML/CSS, Javascript.
Enterprises & organizations of all size should attend to the importance of UX designers, especially those who do not just design beautiful looking visuals but contribute in many other ways to craft good user experience.
Read also: why enterprises & startups in Asia should invest in user experience
Tips: try not to see ‘Design’ as just ‘Visual Design’. For example, you can also ‘design’ how something works, e.g, designing your life. UI designer can unleash creativity juice in other areas like style guide, brand identity, message & voice tone. Similarly, ‘content’ is not necessarily just comprised of text in article, but anything visual and even sound.
Below shows a typical UX design process for launching a product or feature, each phase requires different roles & skill set to implement.
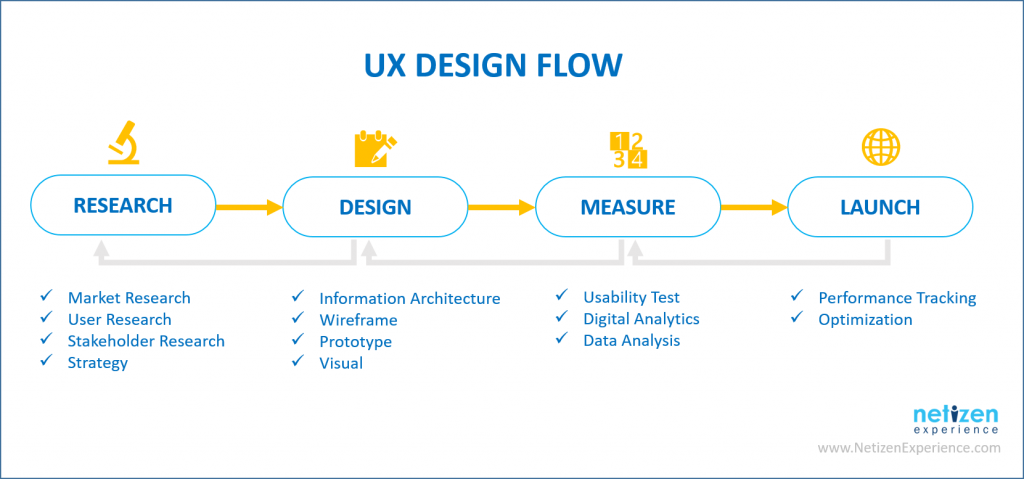
Here’s an easy-to-digest slide for anyone who is new to User Experience to learn about Usability Testing, Information Architecture & Design Principles: www.slideshare.net/sachiew91/newbie-ux-something-i-learned-about-ux
In this article, we are going to take a look at 3 main UX roles that are still commonly remain as a ‘kept secret’ to only the industry practitioners.
Interaction Designer
Other associated roles: UX Designer, Prototyper, UI Designer
Instead of focusing on the aesthetic and all user-facing aspects like a graphic designer, interaction designers focus more on the interaction between users and computers, as well as the end-to-end experience flow. They use visual design tools like Sketch, Adobe AI, and also rapid prototyping tools such as Axure RP, Adobe XD, InvisionApp, & UXPin.
“How this button should look like?’ – Visual Designer
“How this button should respond?’ – Interaction Designer

Interaction Designers require very strong logic thinking skill. They design the steps required by users to perform a task, and how the product should respond throughout the whole user journey. Knowing frontend development, framework (like Bootstrap) and web standard is a plus point because they got better understanding on the production feasibility, and able to work better with developers.
Here are some of the daily tasks of a interaction designer:
- Task Flow
- Wireframe (low fidelity)
- Mockup (high fidelity)
- Prototype (low or high fidelity, usually clickable)
- Discoverability – helps users in knowing what can be done and how to do it
- Feedback – helps users understand what is going on and how to continue
- Visual design*
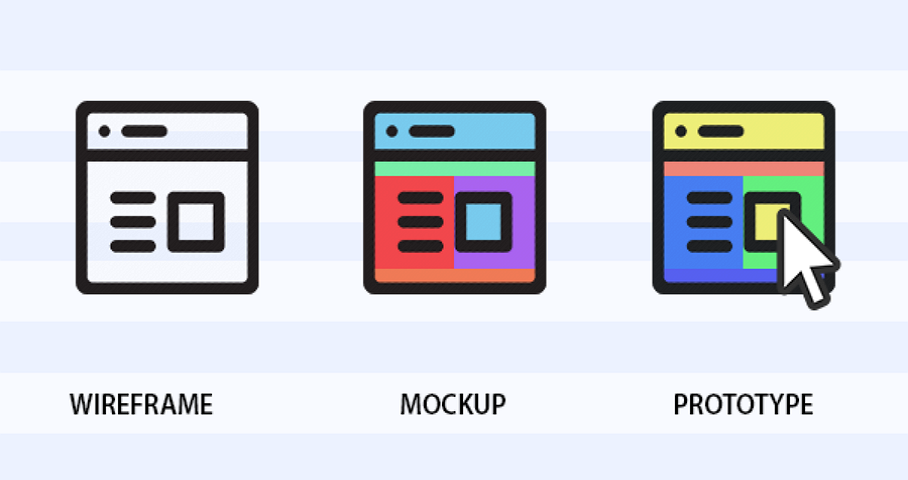
Image Credit: https://www.mockplus.com
*It is not a surprise to see a designer assuming both visual & interaction design roles.
An interaction designer may care about both how a button works and how a button looks. The difference is usually on the sequence. Interaction design generally comes first, visual design will then follow or happen at later stage after usability testing. The idea of creating low fidelity wireframe or prototype is to ensure everyone get the main flow correct before spending time to work on the visual appearance. Similarly, a design should be tested first before going directly to the development team for coding.
In the world of UX, it is very common to see designer doing user research. Although we discuss about 3 main roles separately in this article, it should noted that these tasks and roles are often interchangeable.
User Researcher
Other associated roles: Design Researcher, Data Analyst, Quantitative Researcher, Usability Expert, Information Architect, Conversion Rate Optimizer.
The important and often neglected role in the UX field, user researchers do everything they could to understand user behaviours & needs. They capture both qualitative and quantitative data to help team understand user behaviour. This role is often ventured by those with a background in psychology and HCI (human computer interaction).
Some of the methodologies in conducting user research:
- In-depth User Interview / Focus Group
- Usability testing / User Testing / Guerilla testing (Remote or In-Person)
- Card Sorting, Tree Testing, Task Testing
- Crunch numbers in spreadsheet
- Persona creation, user journey mapping
- Workshop (gamestorming, innovation games).
- Web Analytics / A/B Testing
- Eyes Tracking
- Market Research / Survey
- Expert Review / Heuristic Evaluation


Not only a user researcher can gain data from the target users, but also from related stakeholders: management, employees, departments, customer support team (logs). For researchers that focused more on quantitative data, they’re usually good in making sense of number data, for example: using Excel spreadsheet or able to navigate Google Analytics smoothly. User researchers are also expected to have project management and panel recruitment skills under their belt, as these are essential parts of a user research project.
A good user researchers listen attentively, observe a lot, and know how to ask the right questions, at the right time. Their work do not stop at collecting user data, but also to analyze to uncover meaningful business insight, to prepare business reporting & presentation.
Researchers do not just serve as the advocate for end users (often misled as incurring extra cost to deliver better customer experience), but can also bring win-win to both business and end users. For example, identify business growth and cost reduction opportunities by introducing a better product flow & strategy, often, together with designers & product managers.
Tips: Data do not come just in the form of numbers, but also qualitative feedback & observation.
Product Manager
Other associated roles: Product Owner, Project Manager, UX Lead, UX Manager
“The role of the PM (product manager) is expanding due to the growing importance of data in decision making, an increased customer and design focus, and the evolution of software-development methodologies.” – McKinsey & Co
As the name suggests, they are the ones that manage and responsible for overall product strategy. They are also known as the ‘mini CEO’ or ‘product CEO’ for the digital world. Some of the largest tech company CEOs from Microsoft (Satya Nadella), Google (Sundar Pichai) & Yahoo (Merrisa Mayer) all held the role of ‘Product Manager’ before becoming the top leaders.
Generally, there are 2 types of product manager, one with the technical background which is good for steering products that required high technical knowledge.
On the other hand, there is also product manager from business or design background that can make herself a good supplement to the business.
Amazon likes to hire MBAs from top U.S. business schools as product managers, whilst Facebook prefers one with highly technical background. If a unicorn UX designer is one who can do well in design, research and coding, a unicorn product manager is one who excels in technical knowledge, business acumen and user experience design.
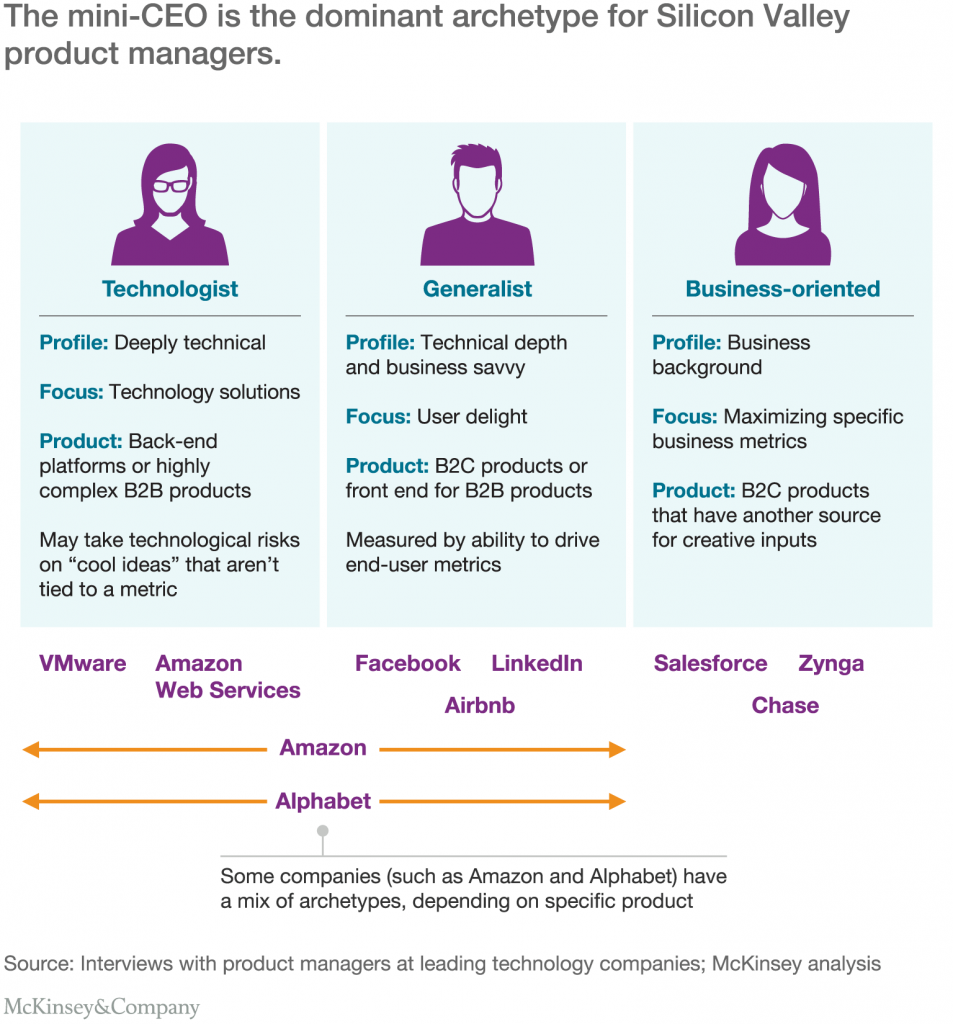
Many are confused with the PM roles, as their responsibilities can be vague. As the main communicator, they set the vision for the team and often serve as the middle man between all relevant stakeholders. Product manager makes sure the baby grows well, by bridging & working with analyst, user researcher, designer, developers. A good product manager is a good sales man, as he has to get management and stakeholders excited about the product.
Prioritization is one of the main tasks of a product manager, they are the ones making tough calls in developing product development road map and the ensuring the team execute it well. Some product manager also assist in user research, design and even coding; however, there are arguments claiming that a good product manager should not get herself involved into these tasks directly. Often, their job is to say ‘No’ to feature request proposed by everyone, and to work on validated leaning for the team.
Many would assume the main KPI of a product manager is their efficiency in shipping product features, yet, it is crucial that product manager helps team in navigating towards the right direction. They minimize ‘waste’ for company; shipping many features on time can be considered as waste if they don’t bring actual value to the team or company.
Shipping features timely might not help to steer company to grow better, but validated learning could. This is why, it is crucial to collect both qualitative and quantity data, that can contribute to validated learnings to make better product and business decisions. Saying so, PMs are important to ensure the team is building the right product, and also building it right.

Image Credits: http://coderchronicles.org/2012/04/24/agile-ux-vs-lean-ux/
A product manager can also help team to do better by adopting Lean UX or Agile UX. Lean UX focuses on validated learning, whilst Agile UX is collaboration centered. As the name suggests, ‘Agile’ helps a cross-functional team to move faster in shipping product, and ‘Lean’ minimizes waste by avoid building the wrong thing.
Good UX is Good Business
You probably now noticed that the 3 roles above play important role in delivering good user experience and improve business at the same time. They work hand in hand together and understand that ‘there is no stupid user, but not so good designer’.
We noticed there are companies who aware of advantages adopting UX strategy and having UX specialist above but many missed out an important thing that UX is a team sport, it is not about hiring few specialist and claiming your company is user or customer centered. It is a shared responsibility of the team or organization, not just the UX team or designers.
A team that has a good UX strategy in place, is able to execute them well when they work inclusively from bottom to top, in and out, with relevant stakeholders: employees from different departments, clients and even external consultants. If UX is yet to be part of your business process, it’s not too late to start to be forward thinking.

