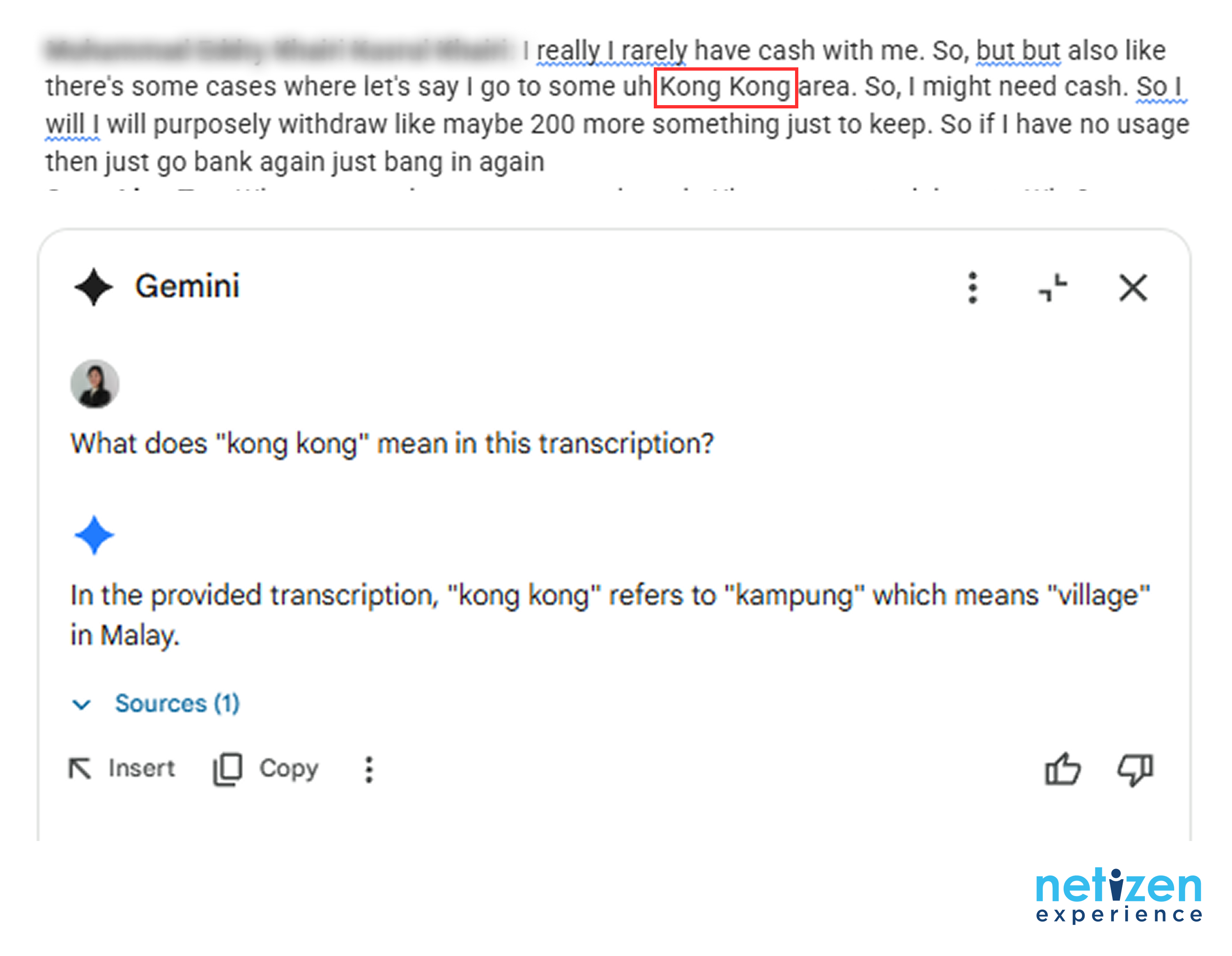
Since user-centric designs are now a core component of modern digital products, it makes sense to ask many more questions about
user experience in design.
One component of user experience (UX) design that is often probed about is UI elements. As the fundamental building blocks of user interfaces, UI elements arguably underpin everything about user experience.
Without thoughtfully designed UI elements, UIs would lack cohesion, functionality, and intuitiveness. This would make it exceedingly challenging for them to navigate and interact with applications effectively.
So, this post aims to go into great detail about UI design elements and their nuances. It also seeks to explain some practical use cases of different UI elements.
What are UI elements?
In simple terms, UI elements are the fundamental building blocks that constitute any user interface. These elements range from small components like buttons, icons, and text fields —to larger elements like image blocks and navigation menus.
In practice, UI elements serve various purposes. For example, guiding user interactions, presenting information, and enhancing the visual appeal of an interface. They tend to provide a sense of familiarity for users, offering a clear path to achieve specific goals or actions.

The importance of UI elements in creating user interfaces
Without a carefully designed set of UI elements, the user experience would be disjointed.
In fact, the overall structure of the product would become fragmented, making it challenging for users to accomplish their goals.
A disjointed UI typically results in disconcertment, confusion, and a lack of engagement as users become lost in a maze of inconsistent and confusing interactions. In stark contrast, a well-crafted set of UI elements creates a cohesive and intuitive experience. This allows users to focus on their intended tasks rather than navigating a disorganised interface.
Overall, intuitive and responsive interfaces guide users through their tasks effortlessly, enabling them to accomplish their goals efficiently. That being said, the implementation of UI elements plays a mission-critical role in shaping the overall user experience.
Basic UI elements
UI elements are the primary means through which users engage with and navigate an interface. UI components have multiple uses and can be applied to many different kinds of projects.
1. Buttons
Buttons are arguably the most fundamental UI elements. They serve as the primary means for users to initiate actions and trigger specific functionalities within an interface.
They are commonly deployed for actions like submitting forms and navigating to different pages. The different types of buttons include:
- Primary buttons: These are the most prominent and frequently utilised buttons. They are often leveraged for the main call-to-action (CTA) on a page.
- Secondary buttons: These buttons are usually deployed for secondary actions or alternative choices.
- Icon buttons: These buttons feature an icon instead of text. They are often used for actions like opening a menu or closing a modal.
2. Icons
Icons are indispensable in visual communication within user interfaces. They serve as compact and recognisable symbols that relay information or functionality.
Additionally, they can enhance the aesthetics of a UI whilst also improving usability by providing visual cues and shortcuts.
Some commonly used icons include:
- Navigation icons such as home, search, menu, and back.
- Action icons like add, edit, delete, share.
- Status icons like success, error, warning, and loading.
3. Text Fields
Text fields are input controls that allow users to enter and edit text within a UI. In practice, they are essential for collecting user data in search bars and forms. For example, names, email addresses, or comments.
The main types of text fields are:
- Single-line text fields: These fields are designed for short, single-line inputs like names or email addresses.
- Multi-line text fields: Also called text areas, these fields allow users to enter longer, multi-line inputs like comments or descriptions.
Navigational UI elements
4. Menus
Menus are critical navigational UI elements that allow users to access different sections and features of an application or website. They come in different forms, for example:
- Dropdown menus: These menus expand to reveal a list of options whenever a user interacts with a menu button or link. They are typically deployed to organise and provide access to a hierarchical structure of content and features.
- Hamburger menus: The hamburger menu is a compact icon (three horizontal lines). Whenever clicked, it reveals a full-screen or sidebar menu. It’s conventionally used where screen real estate is limited.
For effective menu design, consider the following tricks:
- Keep the menu responsive and adaptable to different screen sizes and devices.
- Keep the menu structure simple, with a clear hierarchy of options.
- Always leverage consistent terminology and labelling.
- Ensure that the most frequently used options are easily accessible.
- Provide visual cues, like highlighting the current page or section, to help users orient themselves.
5. Tabs
Tabs allow users to navigate between different sections or views of content. In practice, they help organise UI information into manageable and accessible sections— especially when one has a substantial amount of content that needs to be presented in a structured way. This reduces cognitive overload on users.
Tabs come in two specific forms:
- Horizontal tabs: These are the most common tab form and are typically placed at the top of the content area.
- Vertical tabs: These are less common but can be useful when one has a large number of tabs— or when the content sections require more vertical space.
6. Breadcrumbs
These navigational UI elements display the user’s current location within the application or website’s hierarchy. They provide a visual trail that allows users to understand their position and easily navigate back to higher-level pages or sections.
Breadcrumbs provide a sense of context and orientation within the overall information architecture in different ways, for example:
- On an e-commerce website, breadcrumbs might show the path from the homepage to the current product page. For example, “Home > Category > Subcategory > Product”.
- Breadcrumbs can help users navigate through the site’s hierarchy, such as “About > Team > Leadership”.
Informational UI elements
7. Tooltips
Tooltips provide supplementary context or details when a user hovers over, or interacts with a specific element on the interface. They are expressly designed to enhance user understanding—for example, descriptions, explanations, or instructions—without cluttering the main interface.
They are particularly useful for conveying information about complex features, technical terms, or even user actions. By keeping the main interface clean and uncluttered, tooltips help users focus on the primary tasks. This consequently balances the need for information with the desire to maintain a visually aesthetic and unobtrusive design.
8. Notifications
Notifications are informational UI elements that alert users to important events, updates, or system messages. They can take various forms, for example:
- Toast notifications: These are small, temporary notifications that appear at the top, bottom, or side of the screen. They are often deployed for non-critical updates or confirmations.
- Alerts: These are modal notifications that interrupt the user’s workflow and require immediate attention. For example, error messages or critical system alerts.
Generally, notifications can be utilised to provide timely updates, acknowledge user actions—or even draw attention to important in-app information. Thereby, appreciably enhancing the overall user experience.
9. Progress bars
Progress bars are informational UI elements that visually indicate the status of an ongoing process. For instance, a file upload, form submission, or data loading.
They provide users with a clear understanding of the current state of a task. Thereby, helping to manage their expectations and reduce anxiety during lengthy UI operations.
They can also be used to provide feedback during form submissions. Thus, giving users a visual cue that their input is being processed.
Input UI elements
10. Checkboxes
Checkboxes are input UI elements that allow users to make multiple selections from a set of options. This makes them suitable for scenarios where multiple choices are required.
They are usually deployed in forms, settings, or preference menus where users need to select one or more items.
11. Radio buttons
Radio buttons are input UI elements that allow users to make a single selection from a set of mutually exclusive options. Like checkboxes, they are also often leveraged in forms, settings, or preference menus— where users need to choose one option from a list.
Radio buttons are best for scenarios where users need to choose one option from a list, such as selecting a payment method, a preferred shipping option, or a gender. They are also useful in settings or preference menus where users need to choose a single configuration or preference.
Differences between Checkboxes and Radio Buttons
- Checkboxes allow for multiple selections, while radio buttons are used for single-choice selection from a set of mutually exclusive options.
- Radio buttons are typically leveraged when users can only choose one option from a list, such as selecting a payment method or a preferred language.
12. Sliders
Sliders allow users to adjust a value within a specific range. These UI input elements are commonly utilised for brightness adjustment settings and volume control functions— or any scenario where users need to select a value from a continuous scale. As such, they are particularly useful in media players, image editors, or device settings.
Generally, they provide a visual representation of an available range of a specific function, making it easy for users to understand the minimum and maximum values. In practice, users can make adjustments by dragging the slider handle or clicking on the desired position along the slider.
Containers and layout UI elements
13. Cards
Cards are UI elements that group related information or functionality into a contained, visually distinct unit. They are usually employed to present content in a structured and organised manner.
They allow designers to cohesively present related pieces of information, such as product details, user profiles, or news articles. This structured grouping consequently helps users quickly scan and digest the content. Thus, improving the overall user experience.
Cards are widely used in e-commerce, social media, and content-heavy websites to organise various types of information. For example, products, articles, or user profiles.
14. Modals
Modals are UI elements that display content in an overlay on top of the current interface. They are designed to temporarily interrupt the user’s workflow to draw their attention to a specific task or information.
Conventionally, modals are utilised to present important information, confirm user actions—or even facilitate specific tasks that require the user’s immediate focus.
To effectively leverage modals, consider:
- Using them judiciously to avoid disrupting the user’s flow and causing frustration. They should only be deployed for critical or time-sensitive tasks.
- Ensuring that they’re easy to close, provide clear instructions, and don’t block access to essential functionality.
15. Grids
Grids are layout UI elements that structure content into rows and columns. Grids can be used to establish a clear visual hierarchy, with disparate grid sizes or layouts used to emphasise or de-emphasise certain content.
For the most part, grids allow designers to arrange content, like images, text, or other UI elements— in a structured and predictable manner. This often results in a coherent presentation of information, making it easier for users to ingest the content.
Suffice it to say that the improved readability and ‘scanability’ that grids deliver, guides users’ attention and augment their understanding of presented information.
Interactive UI elements
16. Accordions
Accordions are interactive UI elements that allow users to expand and collapse content sections, thereby, revealing or hiding additional information as needed. They are especially useful for organising and presenting substantial amounts of content in a compact and manageable way.
They constitute a series of expandable and collapsible panels, each containing a title or header and the associated content. Users can click on the header to expand the corresponding panel and view the content, and then collapse it again when they’re done.
This approach appreciably reduces cognitive load and makes it easier for users to find and access the specific information they need.
17. Carousels
Carousels display rotating sets of images, content, or interactive elements— typically in a horizontal or vertical layout. They are usually deployed for showcasing featured content, product images, or promotional banners.
In practice, carousels allow users to view multiple pieces of content or images in a limited space, without taking up too much screen real estate.
As such, they can effectively draw user attention to key content and provide a dynamic, visually engaging experience. However, carousels can also sometimes be problematic if not designed and implemented properly. They may distract users, cause information overload, or make it difficult for users to interact with specific content.
18. Dropdowns
Dropdowns are interactive UI elements that allow users to reveal and select from a list of hidden options. They are commonly deployed to provide access to additional content or functionality within a compact space.
With the ability to expand hidden content without cluttering the main interface, they typically come in two forms, namely:
- Simple dropdowns: These typically contain a short list of options, providing the user with a focused set of choices.
- Mega dropdowns: These dropdowns contain a more extensive and complex set of options, often organised into categories or subcategories. They are utilised when there is a substantial amount of content that needs to be accessible.
Advanced UI elements
19. Graphs and charts
Graphs and charts are advanced UI elements that transform numerical or categorical data into intuitive visual formats. For example, line graphs, bar charts, area charts, pie charts, or scatter plots. Each of these is suited for different types of data and analysis.
They principally seek to enable users to quickly understand and interpret complex information. For example, they help users identify patterns, trends, and relationships within the data. Thereby, making it easier to comprehend and draw insights.
To design readable and effective graphs and charts, always utilise the following:
- Clear labels
- Appropriate scales
- Consistent colour schemes
- Minimise clutter to ensure the data is easily interpreted.
20. Maps
Maps are advanced UI elements that provide interactive geographical representations. In essence, they allow users to explore and interact with location-based information.
They typically incorporate various interactive features. For instance, zooming, panning, and overlaying additional information like markers, routes, or heat maps.
Maps are commonly used in applications like ride-sharing, navigation, real estate, and travel planning. In such applications, geographical context is mission-critical to the user’s experience.
21. Virtual assistants
Virtual assistants are advanced UI elements that leverage artificial intelligence (AI) to provide interactive, conversational support to users within an application or website.
Virtual assistants, like chatbots or voice-based assistants, exploit natural language processing (NLP) to understand user queries and provide relevant assistance.
They provide this assistance in a more natural, conversational manner, rather than relying solely on traditional UI elements.
Best practices for designing UI elements
From clicking on buttons to sign up for an account to seamlessly transitioning between pages, UI elements underpin the user experience. Here are some proven principles to follow when designing UI elements:
- Keep the UI simple and uncluttered, removing any unnecessary elements.
- Always maintain consistency in the visual design, layout, and functionality of UI elements across the entire interface.
- Ensure the UI is accessible to all users, including those with disabilities, by considering factors like font readability, and keyboard navigation.
- Design UI elements that can adapt and scale to heterogenous screen sizes and devices, providing an optimal experience across platforms
Conclusion
UI elements are the most integral part of product design, serving as the core components that shape the entire user experience. For UI designers, having a deep understanding of the above elements and how users engage with them is mission-critical to creating successful digital products.
Reach out to us at Netizen eXperience. With a strong grasp of UI elements, our designers and developers develop interfaces that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also highly responsive, and tailored to the specific preferences of one’s target audience.